- The difference amplifier has two inputs and one output.
- It amplifies the difference between the voltages at the two inputs.
- If the voltage on one input is 10 mV and 15 mV on the other then the difference is 5 mV.
- If the amplifier amplifies by ten times then the output voltage will 5 mV times 10 which equals 50 mV.
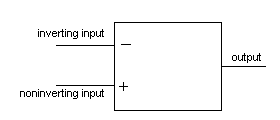
Even if the input voltage is varied there will be no output.
If, when being used as a difference amplifier, there is some interference picked up by both inputs, the interfering signal will not appear at the output because both input signals are the same. Only a difference in inputs will produce an output.

0 comments:
Post a Comment